Operating System Commands by Http Request
Definition
Operating system command execution vulnerabilities are weaknesses that allow malicious users to execute malicious code or induce abnormal behavior within a system using the commands of the operating system.
List of Vulnerability Trigger Points
All pages
When receiving an HTTP request and the operating system executes a command based on the parameter value
Vulnerability Verification Methods
Insert publicly known operating system command execution code into parameter values passed to the web application and verify if the command is executed.
Apache Struts 2 RCE (Remote Code Execution) vulnerability (publicly known operating system command execution code) reference site: https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/WW/Security+Bulletins
The code below utilizes a vulnerability in the Struts 2 framework. If the web page is vulnerable, the result of
3*4, which is 12, will be displayed on the page.<http://host/struts2-blank/example/X.action?action:%25{3\\\\*4}>
Attack Methods
Attack Scenario
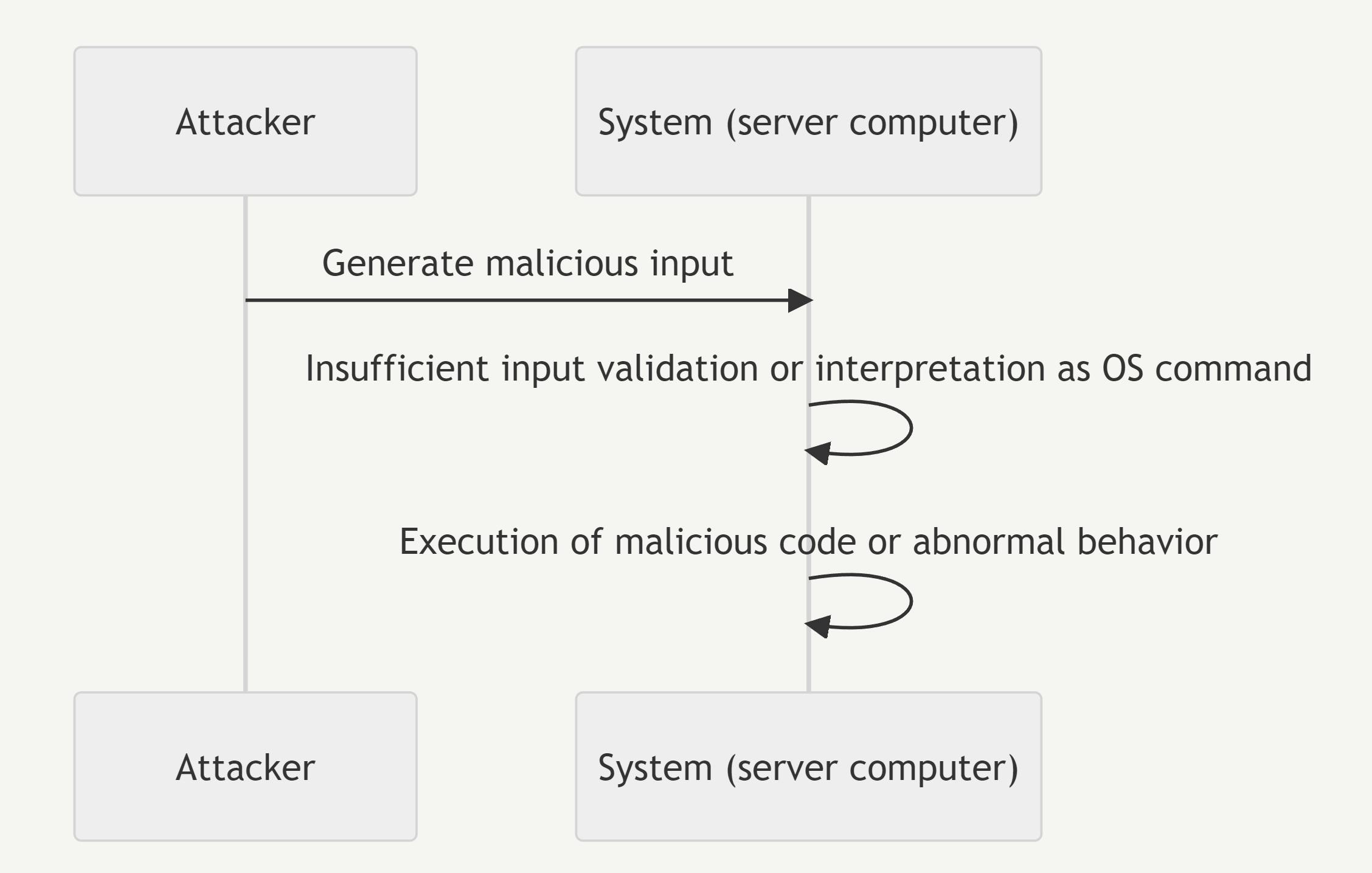
The attacker generates malicious input to be sent to the system.
In vulnerable sections, the input is interpreted as an operating system command or directly passed to a command execution function.
This results in the execution of malicious code or abnormal system behavior.
Process of Occurrence
Detailed Process Explanation
The attacker generates malicious input.
In vulnerable sections, insufficient input validation or incorrect interpretation of external input occurs as an operating system command.
This leads to the execution of malicious code within the system or abnormal system behavior.
Mitigation Measures
Header information restriction: Configure HTTP responses to avoid revealing version information in a few response pages.
HTTP entity: Safely handle command execution by passing user input as arguments to operating system commands.
Input validation and filtering: Transform or restrict user input into a trusted format to prevent malicious code injection.
Permission restriction: Minimize the impact of attacks by limiting the scope of executable commands or restricting the permissions required for command execution.
Use of appropriate command execution functions: Utilize secure operating system command execution functions or libraries that perform security checks.