What is Quick Sort
Definition
One of the fundamental algorithms for sorting in ascending order.
Most important and widely used in any programming language.
O(n log n) complexity, but worst-case scenario can be O(n^2).
To minimize the worst-case scenario, choosing pivot positions randomly can help.
However, if O(n^2) is absolutely not acceptable, another sorting algorithm should be used.
Unstable sort.
Divide and Conquer algorithm.
Easier to implement using recursion.
Structure
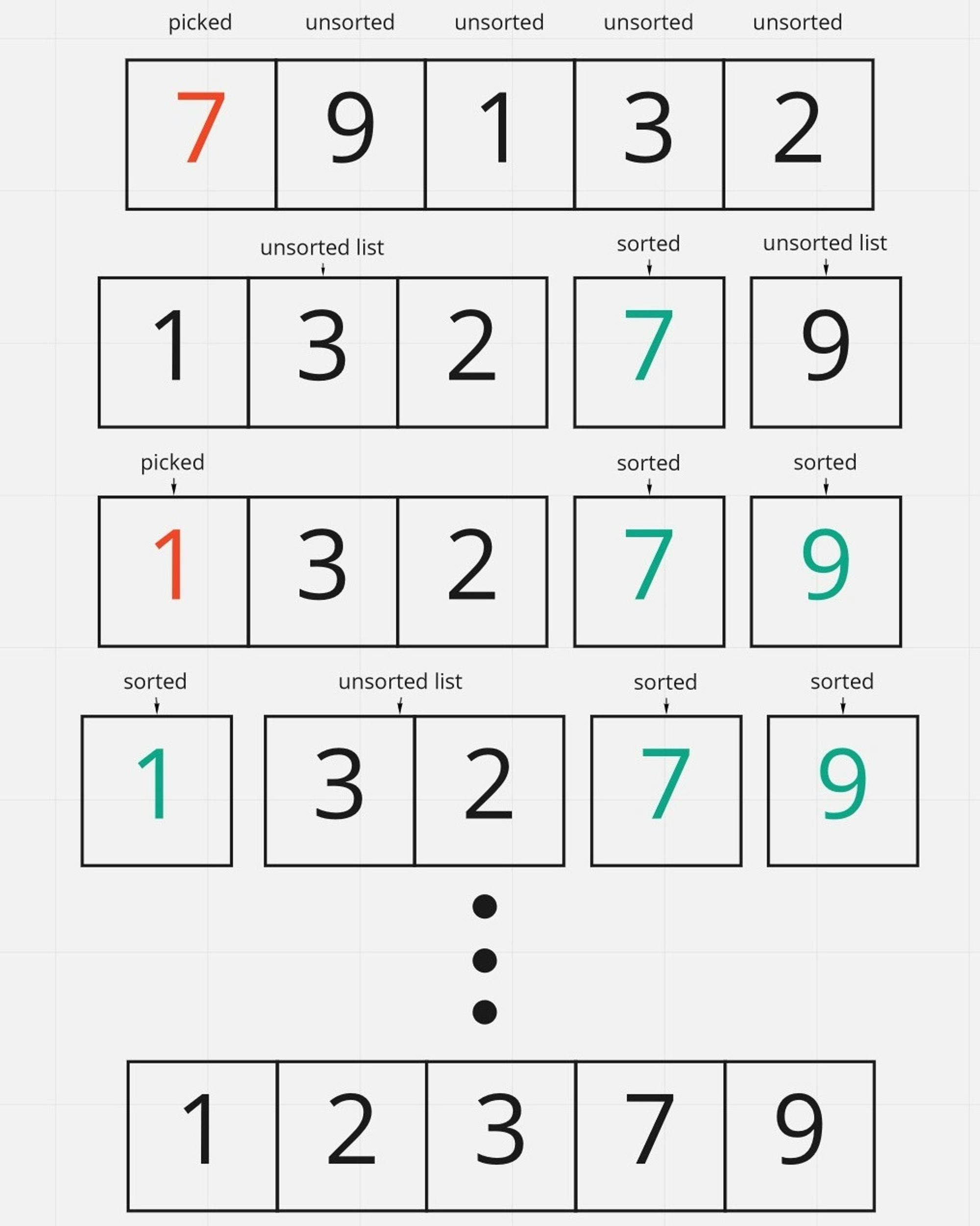
Algorithm
Recursively traverses by dividing into two parts based on the pivot.
Values smaller than the pivot are classified on the left, and larger values on the right. However, this process is carried out without changing the length.
Choose the pivot point. Typically, the rightmost value or the leftmost value is chosen (depends on Lomuto or Hoare partition scheme).
The first value is considered the "selected value."
If the checking value is smaller than the pivot, swap the selected value and the checking value, and move the selected value to the right.
If the checking value is greater than the pivot, move the checking value to the right.
Once the checking value reaches the pivot, swap the selected value and the pivot.
Repeat steps 2 to 6 recursively.
Choosing the pivot value
Lomuto Partition Scheme
Pivot: Rightmost value
Selected value (i) starting point: 0
Checking value (j) starting point: 0
Hoare Partition Scheme
Pivot: Leftmost value
Selected value (i) starting point: 1
Checking value (j) starting point: Rightmost value
Randomly selecting
Java Code - Lomuto Partition Scheme
public static void quickSort(int[] input) {
quickSortRecur(input, 0, input.length - 1);
}
// Quick sort implementation using the Lomuto partition scheme
public static void quickSortRecur(int[] input, int left, int right) {
// Exit condition for quick sort
// Using right >= left would sort in descending order (9,8,7)
// Currently sorted in ascending order (7,8,9)
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
// Partition around the pivot and return its position
int pivotPos = partition(input, left, right);
// Recursively sort the left part
quickSortRecur(input, left, pivotPos - 1);
// Recursively sort the right part
quickSortRecur(input, pivotPos + 1, right);
}
public static void swap(int[] input, int a, int b) {
int temp = input[a];
input[a] = input[b];
input[b] = temp;
}
public static int partition(int[] input, int left, int right) {
int pivot = input[right];
int i = (left - 1);
for (int j = left; j < right; ++j) {
if (input[j] < pivot) {
++i;
swap(input, i, j);
}
}
swap(input, (i + 1), right);
return i + 1;
}
Java Code - Hoare Partition Scheme
public static void quickSort(int[] input) {
quickSortRecur(input, 0, input.length - 1);
}
// Quick sort implementation using the Hoare partition scheme
public static void quickSortRecur(int[] input, int left, int right) {
// Exit condition for quick sort
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
// Partition around the pivot and return its position
int pivotPos = partition(input, left, right);
// Recursively sort the left part
quickSortRecur(input, left, pivotPos);
// Recursively sort the right part
quickSortRecur(input, pivotPos + 1, right);
}
public static void swap(int[] input, int a, int b) {
if (a != b) {
int temp = input[a];
input[a] = input[b];
input[b] = temp;
}
}
public static int partition(int[] input, int left, int right) {
int pivot = input[left];
int i = left - 1;
int j = right + 1;
while (true) {
do {
++i;
} while (input[i] < pivot);
do {
--j;
} while (input[j] > pivot);
if (i >= j) {
return j;
}
swap(input, i, j);
}
}